Too many open files
The problem of "too many open files" will cause failure to open websites and services. The following explains the reasons and solutions:
What is a file handle?
In file I/O, to read data from a file, an application first calls an operating system function and passes the file name, and selects a path to the file to open the file. The function retrieves a sequence number, the file handle, which uniquely identifies the opened file. To read a piece of data from a file, the application needs to call the function ReadFile and pass the address of the file handle in memory and the number of bytes to be copied to the operating system. When the task is completed, close the file by calling the system function
Why does it report "too many open files"?
By default, the default file handle under Linux is 1024. When the concurrency of the server is high or the number of open files is large, it will report "too many open files"
Query the default ulimit:
ulimit -n

How to fix "too many open files" problem
As a temporary solution, execute the following command on the server:
This method does not need to restart the server. Under the current environment variable, it will take effect temporarily. After restarting the server, it will be invalid.
ulimit -n 204800Permanent solution, you need to modify the /etc/security/limits.conf file
cp /etc/security/limits.conf /etc/security/limits.conf_bak echo "* soft nofile 204800" >> /etc/security/limits.conf echo "* hard nofile 204800" >> /etc/security/limits.conf echo "* soft nproc 204800" >> /etc/security/limits.conf echo "* hard nproc 204800" >> /etc/security/limits.confAfter the modification, you need to restart the server to see if it takes effect:
ulimit -nNotice:
The operating system is Debian/Ubuntu. The following configurations are needed
Centos/Redhat Please ignore
Debian/Ubuntulimits.conf does not take effect for root, ordinary users can.Debian/Ubunturoot user-specific configuration:
cp /etc/security/limits.conf /etc/security/limits.conf_bak2 echo "root soft nofile 204800" >> /etc/security/limits.conf echo "root hard nofile 204800" >> /etc/security/limits.conf echo "root soft nproc 204800" >> /etc/security/limits.conf echo "root hard nproc 204800" >> /etc/security/limits.confCheck the configuration results

Modify system limits:
The above modification is the number of file handles opened by a process, but the total limit of the system needs to be modified. For example, the default number of open file handles we set for each process is 1024, but the system limit is 500, and the final number of file handles opened by a process is also 500.
As a temporary solution, execute the following command on the server:
echo 6553560 > /proc/sys/fs/file-maxThe permanent solution requires restarting the server to take effect:
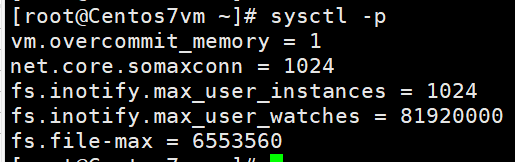
cp /etc/sysctl.conf /etc/sysctl.conf_bak >> /etc/sysctl.conf echo -e "\nfs.file-max = 6553560"After the modification, you need to restart the server to see if it takes effect:
sysctl -p